
Martian Analog (MGS-1 M)
The MGS-1 analog is a mineralogical standard for basaltic soils on Mars, developed based on quantitative mineralogy from the MSL Curiosity rover.
The MGS-1 (Mars Global Simulant) is made by sourcing individual minerals, including a proper treatment of the X-ray amorphous component. It was developed by the University of Central Florida.
The sample was processed at the Instituto de Cerámica y Vidrio (CSIC-ICV) to produce a narrow particle size distribution centered at 3-4 micrometers.

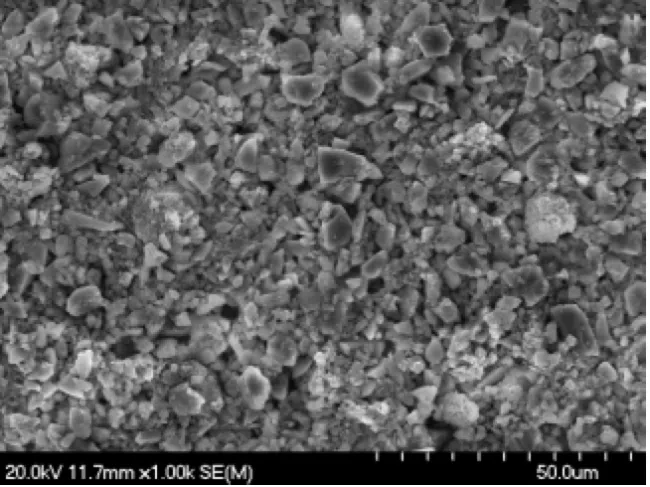
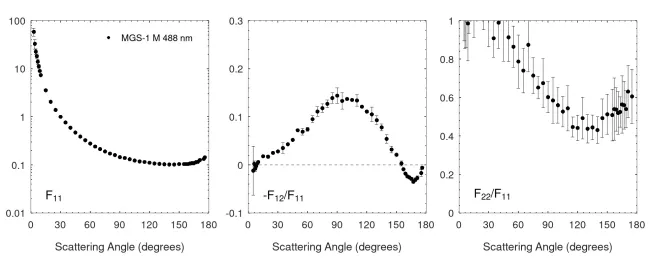
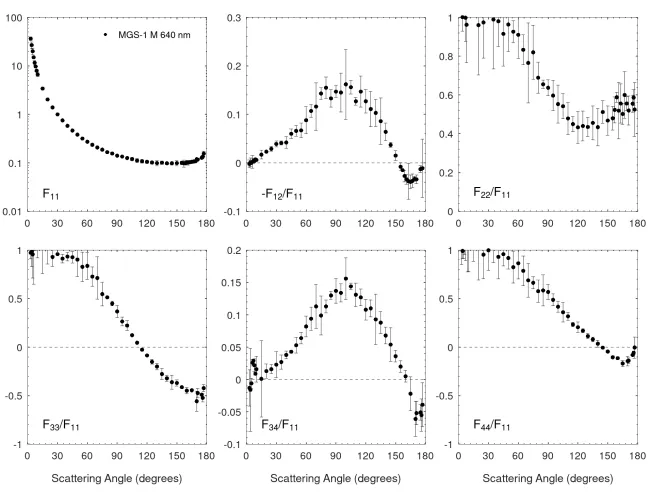
The complex refractive indices of the MGS-1 analogue were retrieved using the MGS-1 XL sample for a wavelength range of 200-2000 nm (see Martikainen et al., 2023). For the wavelengths of the scattering matrix measurements, the values were interpolated as shown by Martikainen et al., (2024).
At 488 nm, n = 1.5 and k =0.00042. At 640 nm, n = 1.5 and k = 0.00043.