
|
From red to blue light: wavelength-dependent photopolarimetry of Mars regolith analogues We studied how the composition and surface roughness of Mars regolith simulants affect the way they scatter polarized light. |
|
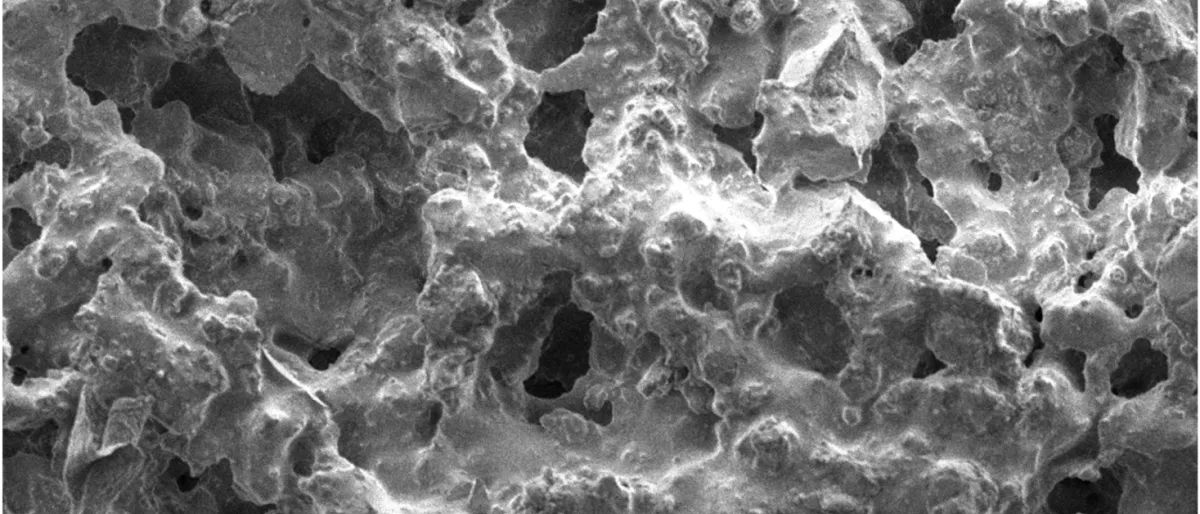
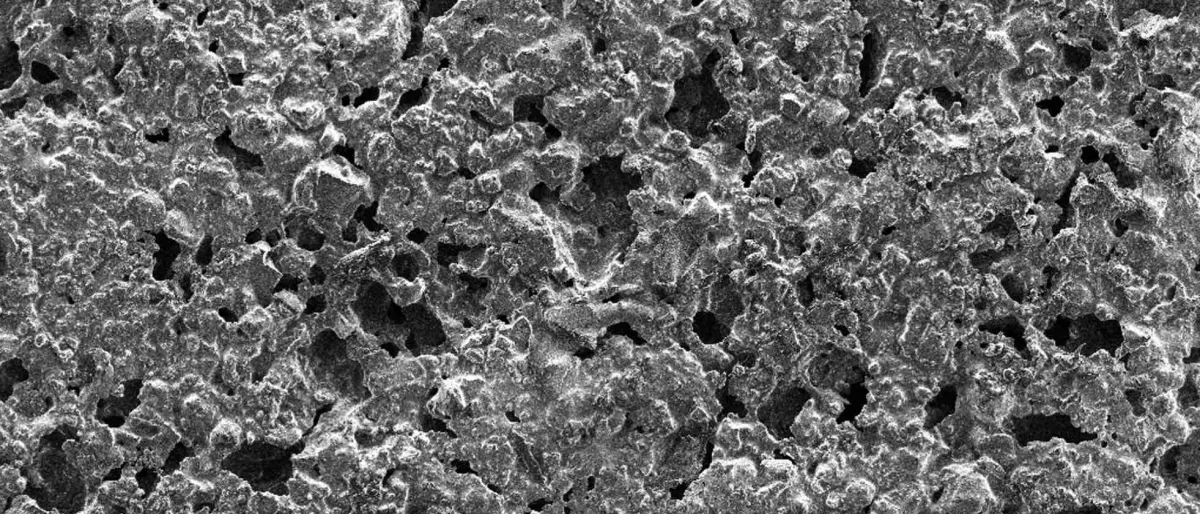
Surface roughness shapes light: new photopolarimetric insights from regolith analogues For the first time, we've performed light-scattering measurements on solid surfaces at the CODULAB laboratory (IAA-CSIC). |

|
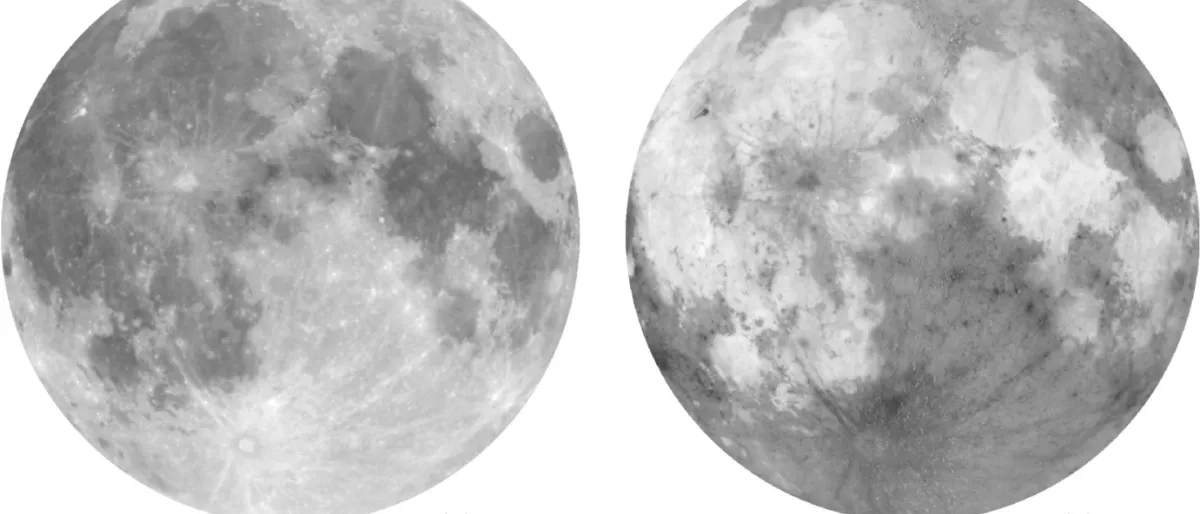
Database of Martian dust optical properties in the UV-vis-NIR The experimental data base of scattering matrices of three well-characterized Martian dust analogues with narrow particle size distributions representative of Martian dust aerosols is used to check the the suitability of hexahedra model particles to reproduce the scattering behaviour of realistic polydisperse irregular particles at 488 and 640 nm. In general, the hexahedra model performs well. |

|
Polarimetry of Solar System minor bodies and planets The study of the polarisation of light is a powerful tool for probing the physical and compositional properties of astrophysical sources, including Solar System objects. In this article, we provide a comprehensive overview of the state-of-the-art in polarimetric studies of various celestial bodies within our Solar System: planets, moons, asteroids, and comets. Additionally, we review relevant laboratory measurements and summarise the fundamental principles of polarimetric observational techniques. |

|
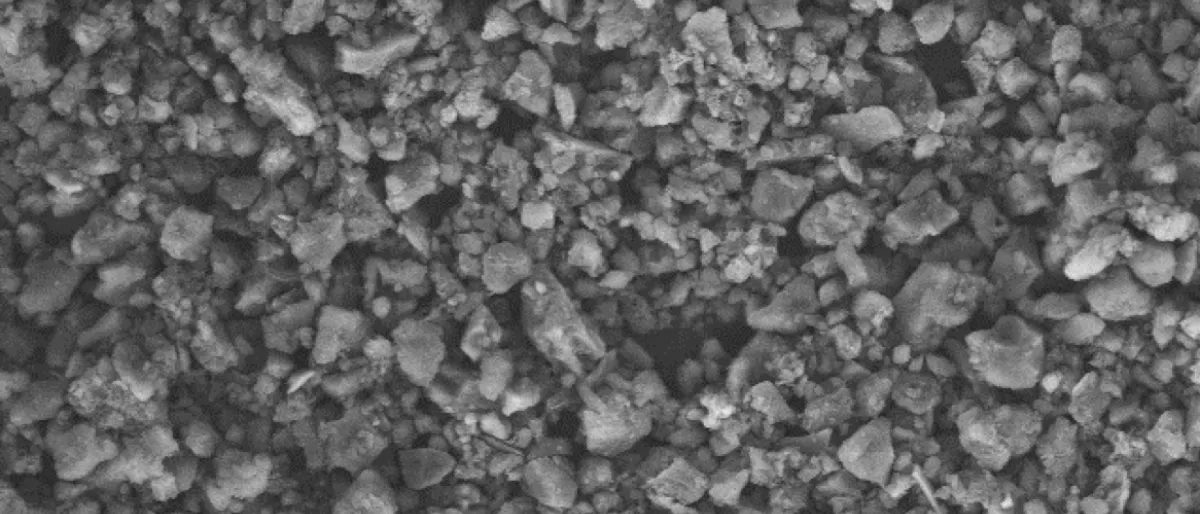
Update Granada–Amsterdam Light Scattering Database We present an update to the Granada–Amsterdam Light Scattering Database, which includes experimental data from both the IAA-Cosmic Dust Laboratory in Granada and the Amsterdam light scattering setup. The updated version features an expanded collection of samples and a more user friendly interface. We have extended the size range of our mineral samples to mm-cm-sized single particles. Additionally, we have added the diffuse reflectance spectra of some of our powder samples and, from these spectra, obtained the corresponding refractive indices (200 nm–2000 nm). |

|
Experimental Scattering Matrices of Martian Dust Aerosols with Narrow Particle-size Distributions We present experimental scattering matrices of the JSC Mars-1, MMS-2, and MGS-1 simulants at 488 and 640 nm. The analogs were processed so that narrow size distributions representative of Martian dust aerosols during different dust cycles were obtained. We find that the forward peak of the phase function depends on particle size as it becomes narrower with increasing size, whereas the side- and backscattering directions depend on both composition and size so that increasing size and decreasing absorption produce a flatter curve. |

|
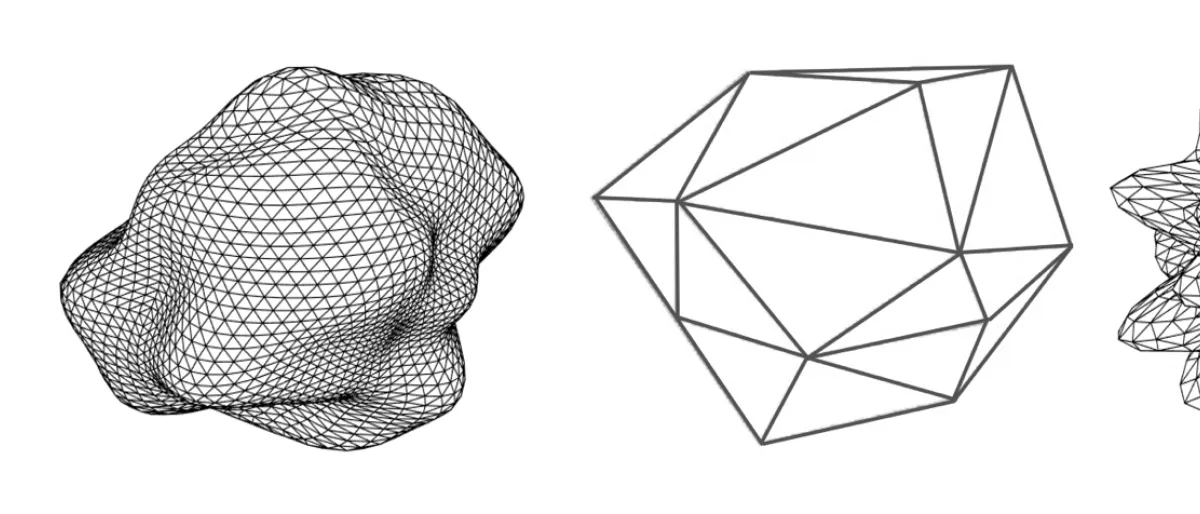
Experimental Phase Function and Degree of Linear Polarization of Light Scattered by Hydrogenated Amorphous Carbon Circumstellar Dust Analogs Astronomical observations of the polarized intensity of scattered visible light have revealed the presence of dust envelopes around different types of evolved stars. These observations have helped determine the diameter and width of dust shells around stars with unprecedented accuracy. Simple geometric particle models are used in order to retrieve dust properties from these observations. |
|
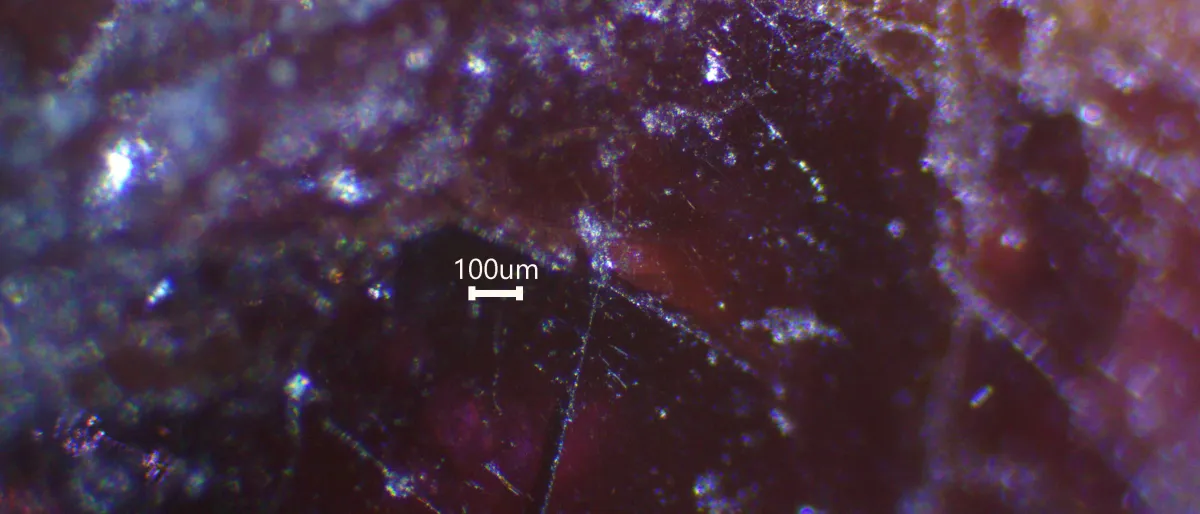
Optical Constants of Martian Dust Analogs at UV–Visible–Near-infrared Wavelengths We present an advanced light-scattering model to retrieve the optical constants of three Martian dust analogs: Johnson Space Center regolith simulant, Enhanced Mojave Mars Simulant, and Mars Global Simulant. The samples are prepared to have narrow particle-size distributions within the geometric-optics domain. We carry out laboratory measurements to obtain the particle-size distributions, shapes, and diffuse reflectance spectra of the Martian analogs deposited on a surface. |
|
Experimental phase function and degree of linear polarization curve of olivine and spinel and the origin of the Barbarian polarization behaviour. We explore experimentally possible explanations of the polarization curves of the sunlight reflected by the Barbarian asteroids. Their peculiar polarization curves are characterized by a large-inversion angle, around 30 degrees, which could be related to the presence of FeO-bearing spinel embedded in Calcium–Aluminum inclusions. In order to test this hypothesis, we have measured the phase function and degree of linear polarization of six samples of Mg-rich olivine and spinel. |
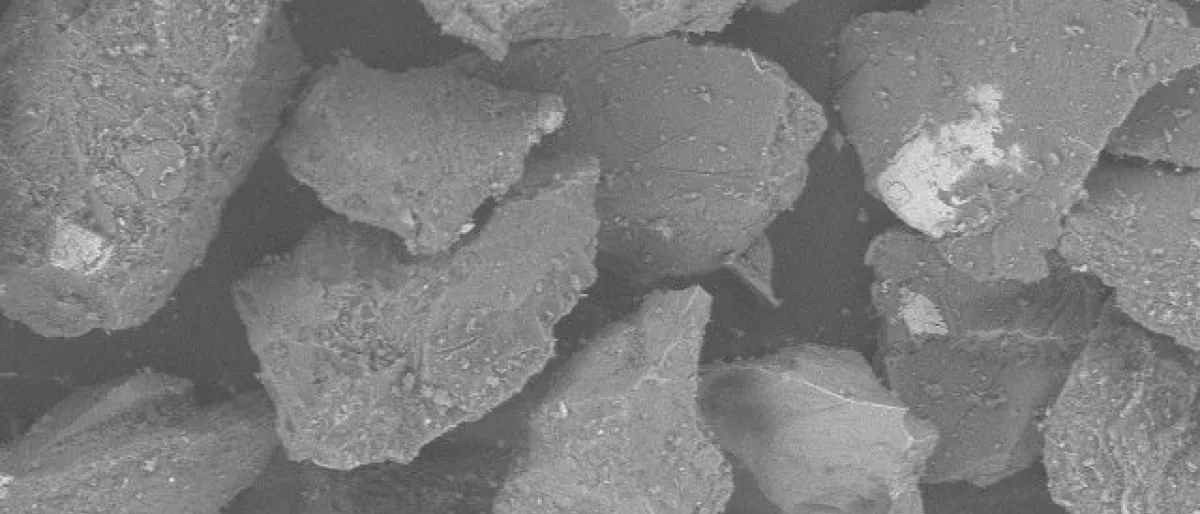
|
Retrieving Dust Grain Sizes from Photopolarimetry We present the experimental phase function, degree of linear polarization (DLP), and linear depolarization (δL) curves of a set of forsterite samples representative of low-absorbing cosmic dust particles. The samples are prepared using state-of-the-art size-segregating techniques to obtain narrow size distributions spanning a broad range of the scattering size parameter domain. |