
Martian analog (MGS-1 XL)
The MGS-1 analog is a mineralogical standard for basaltic soils on Mars, developed based on quantitative mineralogy from the MSL Curiosity rover.
The MGS-1 (Mars Global Simulant) is made by sourcing individual minerals, including a proper treatment of the X-ray amorphous component. It was developed by the University of Central Florida. The bulk sample was processed at the Instituto de Cerámica y Vidrio (CSIC-ICV) to produce a narrow particle size distribution of 20-40 micrometers.
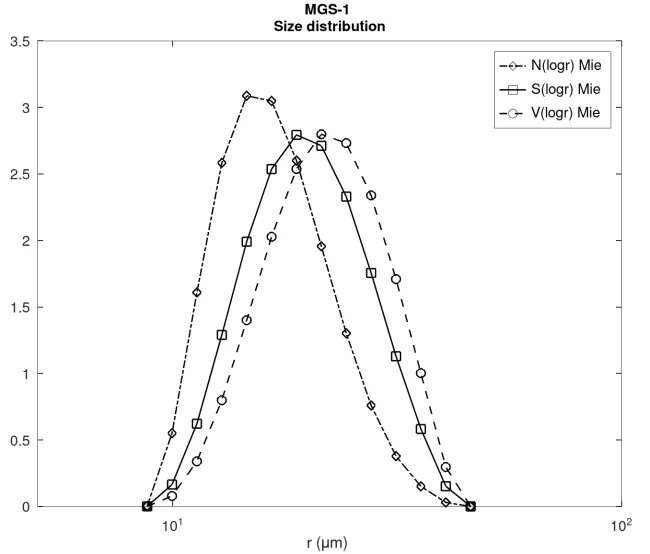
20-40 micrometer narrow size distribution measured at the CSIC-ICV.
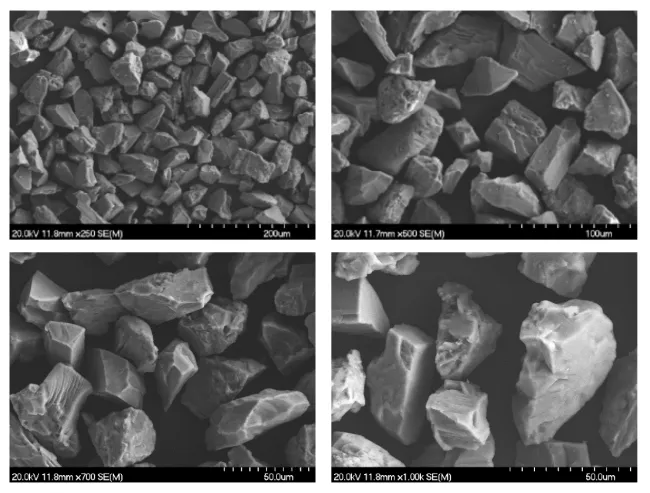
Irregular
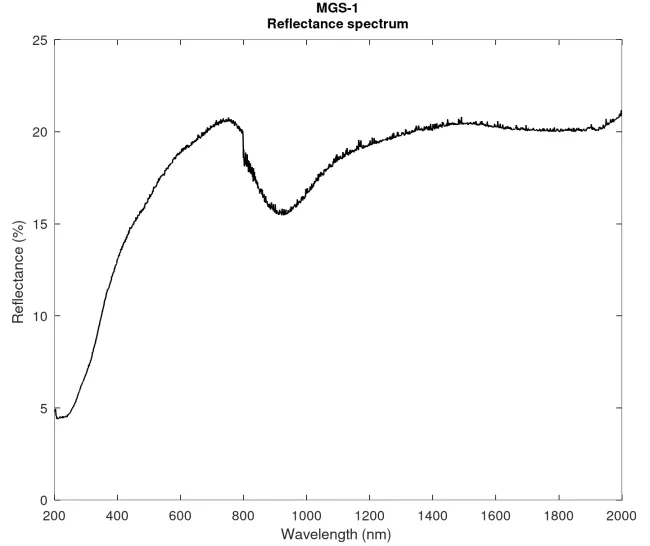
The imaginary parts of the refractive indices, k, we derived for the MGS-1 sample by using the model framework presented in Martikainen et al. 2023, ApJS, with GRS2 particle shapes.
The real part of the refractive index, n, was fixed to 1.5.
The uncertainties were computed by assuming a maximum error of 15% in the measured reflectance over the 200 to 2000 nm wavelength range.